X -ray radiographic absorption imaging is an invaluable tool in medical diagnostics and materials science. For biological tissue samples, polymers or fibre composites, however, the use of conventional X-ray radiography is limited due to... more
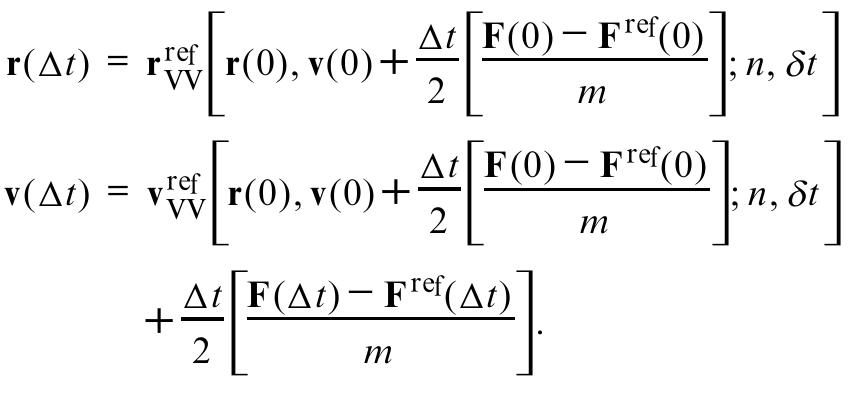
Explicit reversible integrators, suitable for use in large-scale computer simulations, are derived for extended systems generating the canonical and isothermal± isobaric ensem bles. The new methods are compared with the standard implicit... more
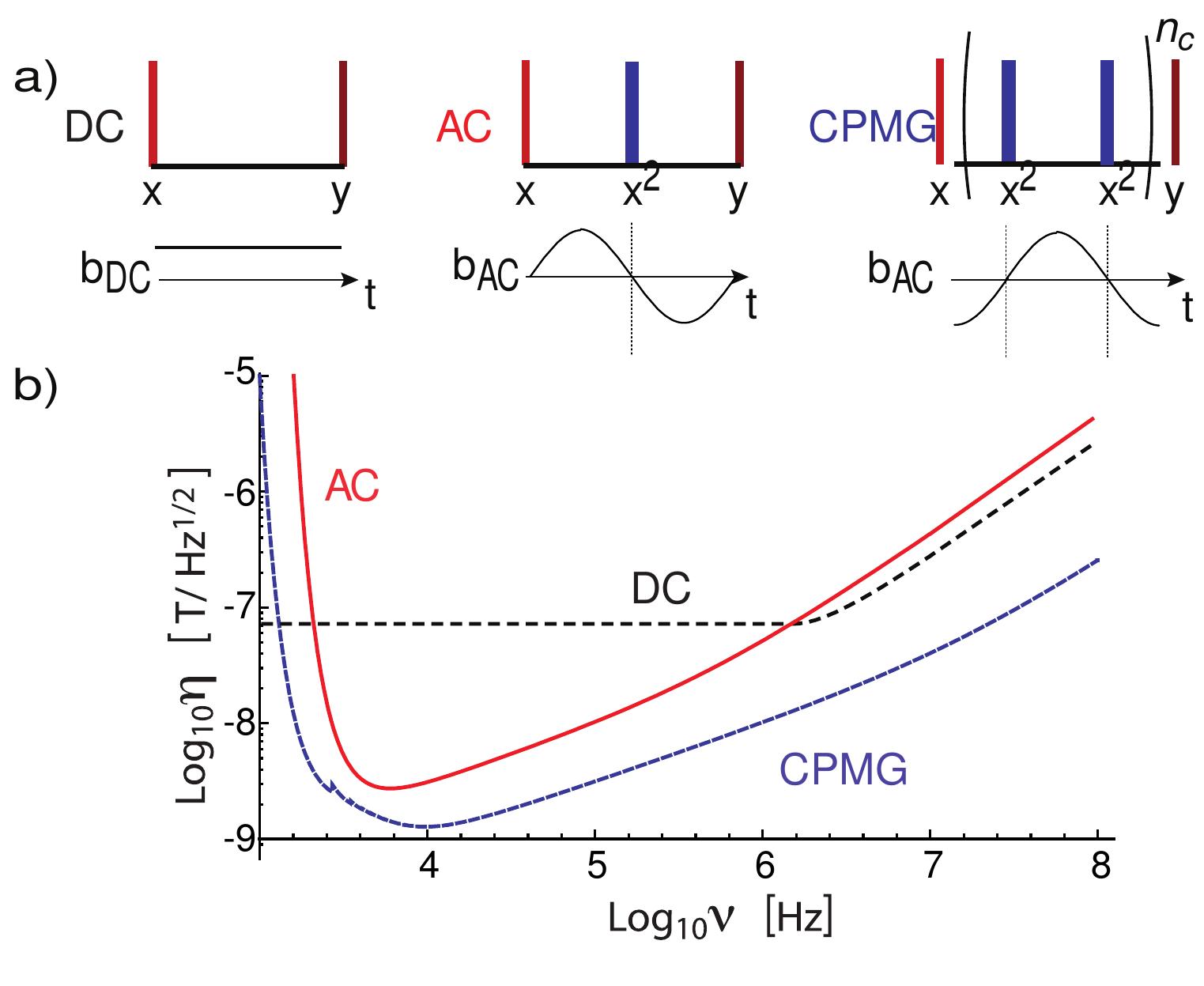
We present a novel approach to the detection of weak magnetic fields that takes advantage of recently developed techniques for the coherent control of solid-state electron spin quantum bits. Specifically, we investigate a magnetic sensor... more
In this paper we write down equations of motion (following the approach pioneered by Hoover) for an exact isothermal-isobaric molecular dynamics simulation, and we extend them to multiple thermostating rates, to a shape-varying cell and... more
Uncovering the hidden regularities and organizational principles of networks arising in physical systems ranging from the molecular level to the scale of large communication infrastructures is the key issue for the understanding of their... more
There is growing interest to investigate states of matter with topological order, which support excitations in the form of anyons, and which underly topological quantum computing. Examples of such systems include lattice spin models in... more
A computationally efficient molecular dynamics method for estimating the rates of rare events that occur by activated processes is described. The system is constrained at "bottleneck" regions on a general many-body reaction coordinate in... more
A recurrent idea in the study of complex systems is that optimal information processing is to be found near bifurcation points or phase transitions. However, this heuristic hypothesis has few (if any) concrete realizations where a... more
† These two authors contributed equally to this work.
In 1929, Leó Szilárd invented a feedback protocol in which a hypothetical intelligence-dubbed Maxwell's demon-pumps heat from an isothermal environment and transforms it into work. After a long-lasting and intense controversy it was... more
Dynamical reaction-diffusion processes and metapopulation models are standard modelling approaches for a wide array of phenomena in which local quantities-such as density, potentials and particles-diffuse and interact according to the... more
Matter-wave interference experiments enable us to study matter at its most basic, quantum level and form the basis of high-precision sensors for applications such as inertial and gravitational field sensing. Success in both of these... more
We consider a one-component fluid in an external potential V(r) at a temperature T and chemical potential /~. The equilibrium density p(r) is given by minimizing the grand potential functional fly[P] = o~[p] + ~ d3rp(r)(V(r) -I~)
A formulation of the n-electron valence state perturbation theory ͑NEVPT͒ at the third order of perturbation is presented. The present implementation concerns the so-called strongly contracted variant of NEVPT, where only a subspace of... more
A mong the variety of roles for nanopores in biology, an important one is enabling polymer transport, for example in gene transfer between bacteria 1 and transport of RNA through the nuclear membrane 2 . Recently, this has inspired the... more
Quantum entanglement [1, 2] plays a vital role in many quantum information and communication tasks . Entangled states of higher dimensional systems are of great interest due to the extended possibilities they provide. For example, they... more
The transfer of spin angular momentum from a spin-polarized current to a ferromagnet can generate sufficient torque to reorient the magnet’s moment. This torque could enable the development of efficient electrically actuated magnetic... more
Recently, condensed matter and atomic experiments have reached a length-scale and temperature regime where new quantum collective phenomena emerge. Finding such physics in systems of photons, however, is problematic, as photons typically... more
A description of the ab initio quantum chemistry package GAMESS-UK is presented. The package offers a wide range of quantum mechanical wavefunctions, capable of treating systems ranging from closed-shell molecules through to the species... more
We report the observation of nonclassical light generated via photon blockade in a photonic crystal cavity with a strongly coupled quantum dot. By tuning the frequency of the probe laser with respect to the cavity and quantum dot... more
Fermionic alkaline-earth atoms have unique properties that make them attractive candidates for the realization of novel atomic clocks and degenerate quantum gases. At the same time, they are attracting considerable theoretical attention... more
We present a new relativistic formulation for the calculation of nuclear magnetic resonance ͑NMR͒ shielding tensors. The formulation makes use of gauge-including atomic orbitals and is based on density functional theory. The relativistic... more
The y-expansion as introduced by Barboy and Gelbart is applied to a system of hard ellipsoids-of-revolution. The expansion is truncated after the third order term yielding an approximate theory requiring the second-and third-virial... more
A striking feature of bilayer graphene is the induction of a significant band gap in the electronic states by the application of a perpendicular electric field 1-6. Thicker graphene layers are also highly attractive materials. The ability... more
The conventional cold, particle interpretation of dark matter (CDM) still lacks laboratory support and struggles with the basic properties of common dwarf galaxies, which have surprisingly uniform central masses and shallow density... more
Qubits, the quantum mechanical bits required for quantum computing, must retain their quantum states for times long enough to allow the information contained in them to be processed. In many types of electron-spin qubits, the primary... more
Magnetic reconnection releases energy explosively as field lines break and reconnect in plasmas ranging from the Earth's magnetosphere to solar eruptions and astrophysical applications. Collisionless kinetic simulations have shown that... more
Molecular Physics, 1992. Vol. 76, No. 6, 1319-1333 Vapour liquid equilibria of the Lennard-Jones fluid from the NpT plus test particle method By AMAL LOTFI, JADRAN VRABKC and JOHANN FISCHER Institut für Thermo-und Fluiddynamik,... more
Devices that harness the laws of quantum physics hold the promise for information processing that outperforms their classical counterparts, and for unconditionally secure communication 1 . However, in particular, implementations based on... more
Routing information through networks is a universal phenomenon in both natural and manmade complex systems. When each node has full knowledge of the global network connectivity, finding short communication paths is merely a matter of... more
In this article we review state-of-the-art methods for computing vibrational energies of polyatomic molecules using quantum mechanical, variationally-based approaches. We illustrate the power of those methods by presenting applications to... more
Experiments on single nitrogen-vacancy (N-V) centres in diamond, which include electron spin resonance, Rabi oscillations, single-shot spin readout and two-qubit operations with a nearby13C nuclear spin, show the potential of this spin... more
We review the current status of quantum chemistry as a predictive tool of chemistry and molecular physics, capable of providing highly accurate, quantitative data about molecular systems. We begin by reviewing wave-function based... more
At timescales once deemed immeasurably small by Einstein, the random movement of Brownian particles in a liquid is expected to be replaced by ballistic motion. So far, an experimental verification of this prediction has been out of reach... more
interfaces occurs in a wide variety of atmospheric, oceanic, geophysical and astrophysical flows. The Rayleigh-Taylor instability, a process by which fluids seek to reduce their combined potential energy, plays a key role in all types of... more
Magnetic monopoles have been predicted to occur as emergent fractional quasiparticles inside pyrochlore spin ice, a frustrated magnetic insulator. Experimental signatures of such emergent monopoles accompanied by Dirac strings have been... more
Einstein's general theory of relativity establishes equality between matter-energy density and the curvature of spacetime. As a result, light and matter follow natural paths in the inherent spacetime and may experience bending and... more
In this article we demonstrate that the Gibbs ensemble and the canonical ensemble are equivalent in the thermodynamic limit. Furthermore, we discuss some interesting aspects of the method when applied close to the critical point. We show... more
Magnetic insulators have proved to be fertile ground for studying new types of quantum many body states, and I survey recent experimental and theoretical examples. The insights and methods transfer also to novel superconducting and... more
A splash is usually heard when a solid body enters water at large velocity. This phenomenon originates from the formation of an air cavity during the impact. The classical view of impacts on free surfaces relies solely on fluid inertia;... more
Generating attosecond pulses has required a radically different approach from previous ultrafast optical methods.
Dissociative recombination is a cornerstone reaction in the synthesis of interstellar molecules and plays an important role in the ionised layers of the atmospheres of the Earth, other planets, and their satellites. The studies of... more
Similarity transformed equation-of-motion coupled-cluster theory: Details, examples, and comparisons
The Similarity Transformed Equation of Motion Coupled Cluster (STEOM-CC) method is benchmarked against CC3 and EOM-CCSDT-3 for a large test set of valence excited states of organic molecules studied by Schreiber et al. [M. Schreiber, M.R.... more



![Martyna, Tuckerman and Klein (MTK), following Nosé [3] and Hoover [4] employed a chain of Nosé—Hoover thermostats to drive a dynamical system t generate canonically distributed positions r;, and momenta p;. The equations o motion MTK proposed are as follows [6]:](https://figures.academia-assets.com/30910585/figure_001.jpg)
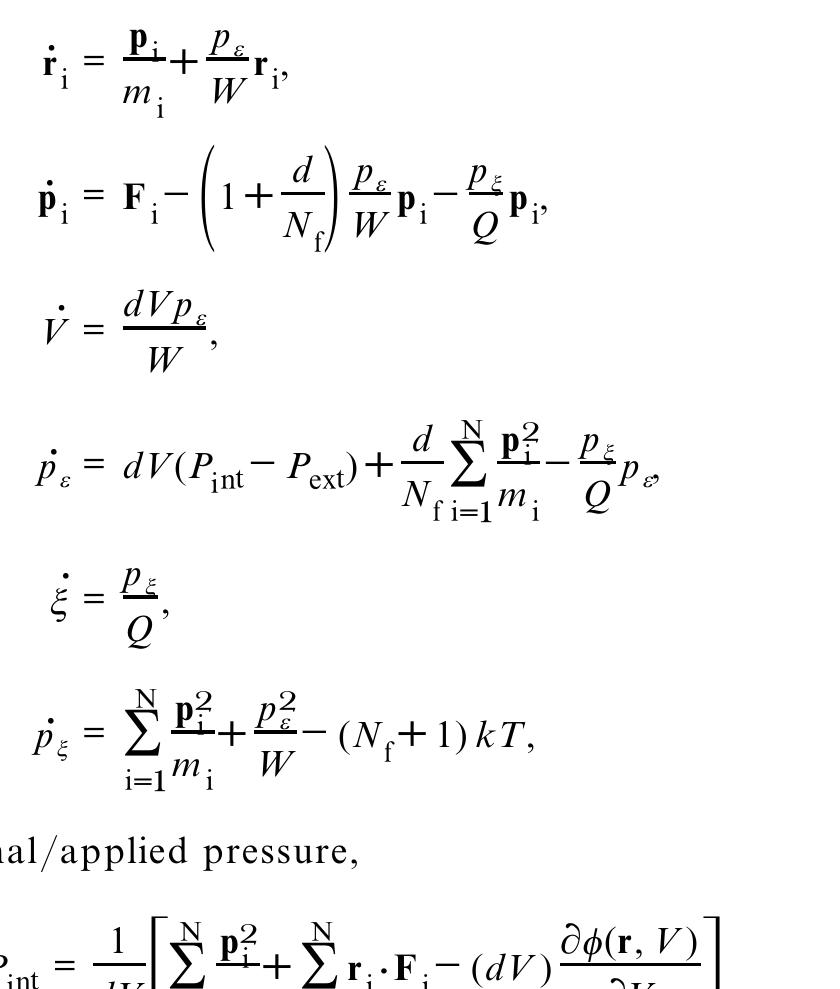




![Note, a time-saving feature has been employed. The effect of the operator exp CL yc’ j At/2n,) is to scale the particle velocities by the factor exp (— Ve Wj At/2n,). The only coupling of the particle velocities to the thermostat variables occurs through the total atomic kinetic energy (AKIN), which appears in the force on the first thermostat G,. Therefore, a velocity scaling factor can be accumulated and applied to the velocities at the end of the procedure. In addition, the total particle kinetic energy can be evolved by multiplying by the factor exp (— Ve, w, At/2n,) at each step in the iteration. The entire propagator may be implemented by performing the procedure defined in equation (35) before and after performing the procedure defined in equation (23). A fifty line Fortran code based on this algorithm is presented in appendix A. The reversible NVT integration method is not altered significantly if an arbitrary set of constraints is placed on the particle degrees of freedom. The operator exp (IL yy At/2n,) acts by scaling the particle velocities by factors of exp (— ve W; At/2n,) at each step in the NHC multiple time step procedure (exp [ax(0/0x)|x = x exp [a]). This scaling does not effect a given constraint if it is initially satisfied (do,/dt = Divi V., 0, = 0). Therefore, the new integration algorithm can be made consistent with a set of constraints by adding the iterative Shake/Rattle algorithm to the velocity—Verlet step in the usual way [18, 19]. Alternatively, the equations of motion generated by Gauss’ principle of least constraint can be integrated reversibly in some](https://figures.academia-assets.com/30910585/figure_007.jpg)


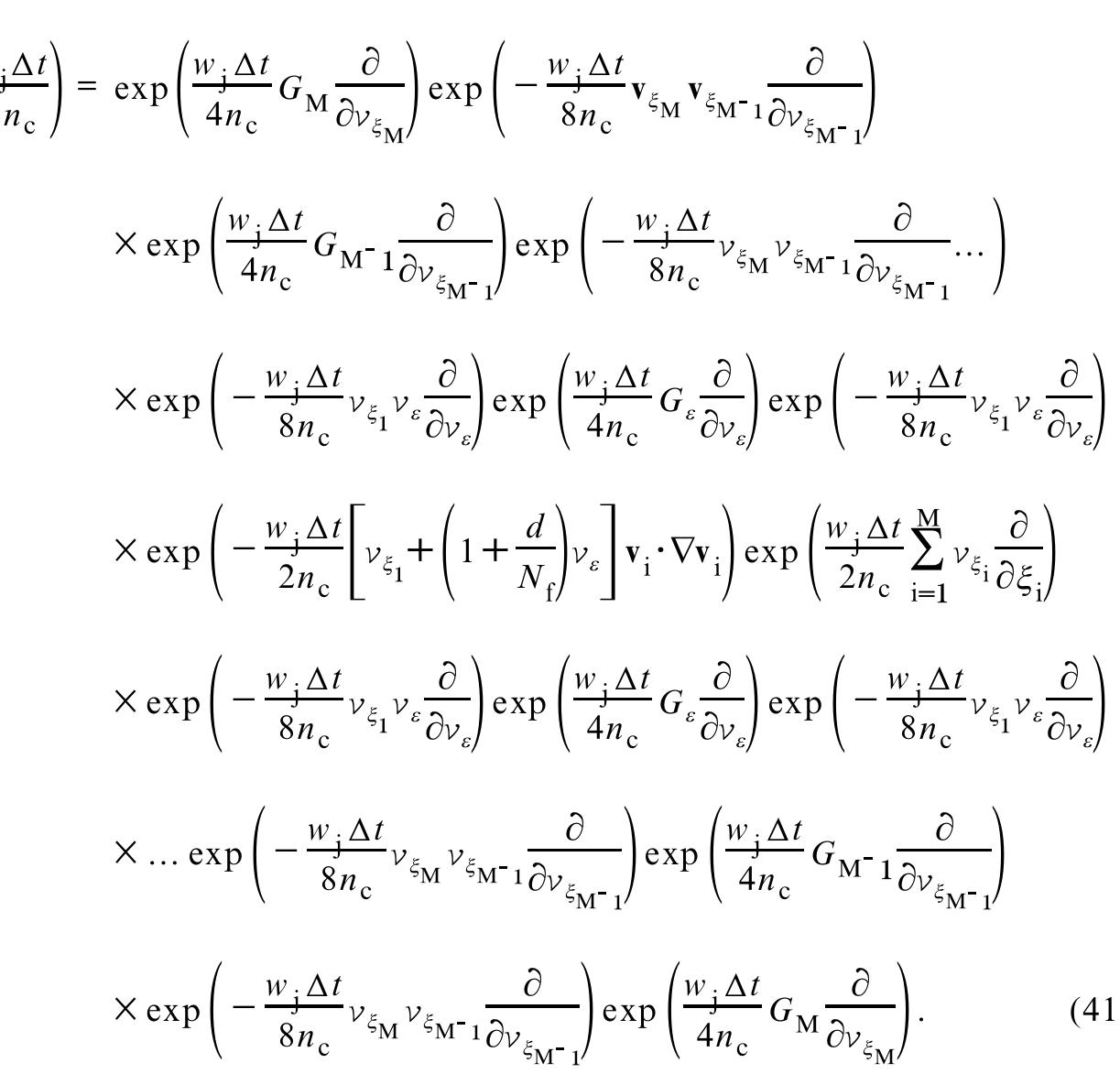




![In the case of NVT-RESPA, the operators, iL p iLs and iL., retain exactly the sam definitions as for the NVE-RESPA case. Therefore, NVT-XO-RESPA is simply NVE RESPA modified by the application of the extended system operator exp (iL yy At/2 at the beginning and the end of each large time interval At. NVT-XI-RESPA is onl slightly different. It can be defined as an n time step, reversible, NVT integration of th reference system wherein the particle velocities are modified by the difference betwee the true force and reference force (as in NVE-RESPA) after/before the first /fing (2nth) application of exp (iL\,,.51/2). A Fortran implementation of NVT-XO-RESP. and NVT-XI-RESPA is provided in appendix E. slow compared with these motions (i.e., through the masses Q and W). Two exceptions are in path integral molecular dynamics where it is most efficient to have the extended system variables (the thermostats) evolve on the same time scale as the vibrations of the path integral chain polymer [22] and in NPT simulations of systems with stiff bonds (atomic virial) that give rise to a strong coupling between the system and the baro/thermostat velocities. The XO-RESPA factorization may also be applied to the long-range force problem. However, it may be the case that the extended system variables have been chosen to evolve on a time scale close to that of the short-range forces. Such systems require a different RESPA factorization. If the motion prescribed by exp GLagaret') occurs on the same time scale as that Anant nas Sac Het asta FARA SIA & Weel Dee RA sasat th dla dad BRAG ARE Ae](https://figures.academia-assets.com/30910585/figure_019.jpg)
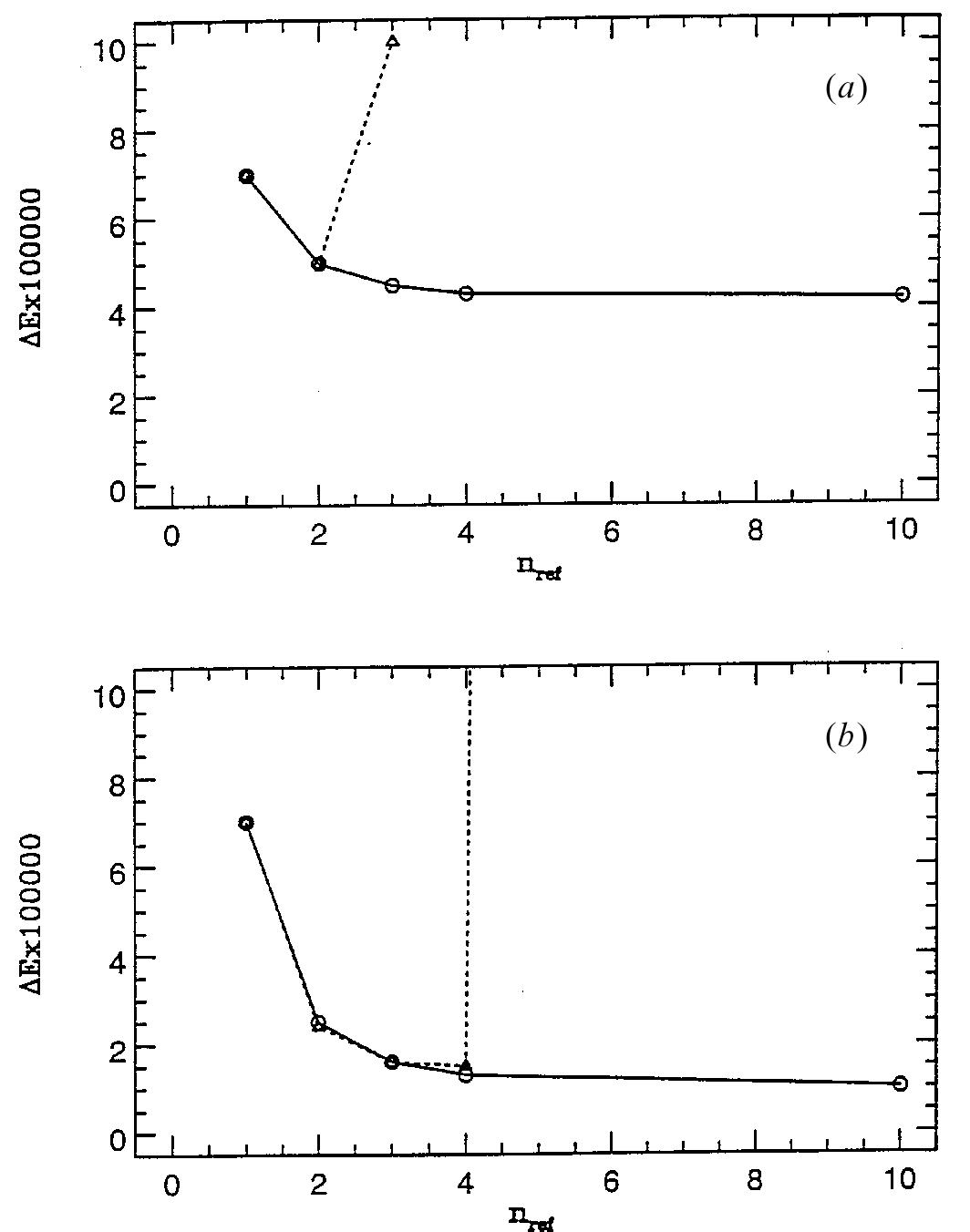
![igure 1. The deviation of the conserved quantity from its initial value, AE(t) = [E(t)— E(0)]/ [E(0)], for a harmonic oscillator undergoing Nosé—Hoover chain dynamics (m = 1, o = 1, Q,,= 1), plotted versus time as a function of the number of inner steps n, used in the NHC multiple time step procedure, equation (29). Yoshida/Suzuki integration is denoted by n.Xn,, for a total of n.X n,, inner steps.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/30910585/figure_020.jpg)



![steps (all intramolecular interactions in the reference force but no intermolecular terms). Similar results have been reported elsewhere for NVE-RESPA [21]. The Andersen—Hoover equations can be integrated at the same level of accuracy by using NPT-XI-RESPA (see table 1). Note that, in constant pressure simulations, NPT-XO- RESPA is inappropriate as NPT-XI-RESPA integration with a sufficient number of NHC multiple time steps {n, = 3,ny, = 3} is required to give the correct average volume (the volume generated by the small time step calculations).](https://figures.academia-assets.com/30910585/table_001.jpg)


























![Because the nuclear-weight function should partition the integrand into atom-like partitions, the Hirschfeld partitioning offers itself as an obvious contender to the Becke nuclear-weight function. Becke did mention exponential nuclear-weight functions in his original paper but did not elaborate on his reasons for rejecting them. The Hirschfeld nuclear-weight function [63] is defined as First we consider the Becke nuclear-weight function, which is defined as The integration of the ‘atomic density’ now boils down to a one-dimensional integration of an exponen- tial function for which a grid can be defined which integrates this exactly. Each grid point accounts for a particular section of the z axis. To obtain reference results each section can be integrated with multiple points as well. Having established these grids, we consider integrating the molecular density along the line using Becke-type quadratures.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/47773123/figure_001.jpg)









![where Hp is the MCSCF Hamiltonian.The straightfor- ward way to solve these eigenvalue equations is to assume that there is a set of vectors x that are eigenvectors of the matrices S and E simultaneously. In that case direct methods based on the Davidson diagonalization method can be applied. However, the existence of such a set of vectors can only be guaranteed if the reference wavefunction corresponds to a ground-state MCSCF wavefunction. where + and s refer to orbitals, « describes the time dependence of the orbitals, m refers to states in the orthogonal complement of the MCSCF wavefunction, and 2% describes the time dependence of the N electron states. After the derivation sketched above and described in detail by Fuchs [26] the following eigenvalue problem is obtained:](https://figures.academia-assets.com/47773123/table_004.jpg)


![Figure 1. Convergence of the coupled-cluster hierarchy for the water molecule in the cc-pVDZ basis. At each level of theory, the error in the energy has been plotted relative to the FCI energy in the same basis [1].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/46509503/figure_001.jpg)
![Figure 2. Normal distributions of errors in atomisation energies (kJ mol~'), calculated with all electrons correlated, without (grey) and with (red) X~?-extrapolation of Equation (29). For details on systems, see [1]. which contains unknown terms of order X* and higher only. Such an extrapolation may significantly improve the accuracy of an orbital-based calculation of the electronic energy, reducing the error in the calculation significantly, often by an order of magnitude or more. In Figure 2, we have plotted normal distributions of errors in atomisation energies for the standard models](https://figures.academia-assets.com/46509503/figure_002.jpg)
![Figure 3. Errors in the total energy of molecular hydrogen against the number of basis functions for KW Mi and ECG x expansions. The linear parameters, c; and non-linear parameters A), s; are determined by variationally minimising the Rayleigh—Ritz quotient for the energy. The motivation for this choice of expansion is twofold. First, Boys [49] and Singer [50] have shown that all of the necessary Hamiltonian matrix elements are easily evaluated and are not much more complicated than two-electron GTO Coulomb integrals. Second, the ECGs are highly flexible and, with careful optimisation of the non-linear parameters, the rate of convergence with the number of ECGs is as fast as that of the Hylleraas approach [57]. This is illustrated in Figure 3 for molecular hydrogen, where we plot the error of the BO nonrelativistic energy against the number of terms in the ECG and KW wave-function expansions [41]. The success of the ECG method depends crucially on the ability to optimise a large number of non-linear parameters. The optimisation must be reliable and efficient since repeated re-evaluation of the n-electron integrals is expensive. The method of choice is an iterative use of Powell’s conjugate derivative method, where subsets of n(n+7)/2 parameters belonging to individual ECGs](https://figures.academia-assets.com/46509503/figure_003.jpg)
![method is avoided, enabling a treatment of more general systems. In the GGn method, the many- electron integration is performed analytically and the WO functional is used to avoid four-electron integrals. The form of the pair-function expansion is similar to R12 theory and a dual basis is used, comprised of the conventional set of virtual orbitals and a set of GTGs constructed from orbital pairs with an attached correlation factor. The hierarchy of methods GGO, GG1, GG2, respectively, are defined by the set of orbital pairs used in the geminal basis [117,118]: ihese expansions May equally be viewed as a specilic choice of centres and exponents in the GTG expansion of Equation (47): the centres P,, and Q, are fixed at the nuclei and the exponents a, and £6, are those of a standard Gaussian orbital basis set. The set of exponents y,, are usually taken to be an even-tempered series of six or nine terms. Since the exponents and centres are fixed, the convergence is much slower with respect to basis size than for the original GTG method, and polynomials representing much larger angular- momentum quantum numbers occur. However, because the conventional virtual orbital pairs and standard basis sets are employed, one ensures that the expansion is capable of yielding a good overall description of w;, and the additional GTGs act to improve the correlation description. In particular, they are capable of describing the short-range r,. depen- dence of the wave function near the cusp.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/46509503/figure_004.jpg)
![Figure 4. Basis-set error of CCSD Hl, CCSD(R12) @ and CCSD(F12) A correlation energies of Ne using aug- cc-pV XZ basis sets. When the amplitudes are determined in this way, the method is referred to as CCSD(R12) or CCSD(F12). Detailed expressions for the CCSD-R12 method without an auxiliary basis set have been presented by Noga and co-workers [93,174] and the CCSD(R12) formula with the inclusion of a CABS basis have been derived by Hattig and co-workers [132,134,135,137]. The basis-set errors in the correlation energy of Ne for the CCSD, CCSD(R12) and CCSD(F12) methods are plotted in Figure 4 for the orbital basis sets aug-cc- pVXZ with ¥=2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. As a general rule, the accuracy of a CCSD(F12) calculation using an orbital basis with cardinal number YX is better than that of a conventional calculation using a basis with X¥ +2. For a given orbital basis, a CCSD(F12) calculation is only a factor of three times more expensive than the CCSD method and is therefore a practical tool for performing meaningful coupled-cluster calculations on large systems in small orbital basis sets. A perturbative triples correction may be computed from the T, and 7) amplitudes in the same way as for conventional CCSD(T) and Tew et al. have demonstrated that](https://figures.academia-assets.com/46509503/figure_005.jpg)



![Table 2. Small corrections to CCSD(T)-R12 atomisation energies (J~ Do in kJ mol~') of selected hydrocarbons. Data taken from [104]. ,Frozen- core fe-CCSD(T)-R12 value. >Contribution due to including core orbitals (ae-CCSD(T) treatment). ‘Harmonic zero-point vibrational energy. “Anharmonic correction to the harmonic zero- point vibrational energy. Correction due to the spin-orbit splitting of the °7P state of atomic carbon. ‘Relativistic one-electron Darwin correction. ®Relativistic one-electron mass—velocity correction. "NIST-JANAF thermochemical tables [177].](https://figures.academia-assets.com/46509503/table_002.jpg)
![“From [103]. >Frozen-core cc-pVTZ level, taken from [178]. “Frozen-core cc-pVDZ level, taken from [178]. “From ae- and fe-CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pCV5Z calculations, taken from [178]. “From [103]. ‘From [179]. See [180] for HF. Table 3. Best estimates of the harmonic vibrational frequencies (in cm~') of the diatomic closed-shell molecules HF, N>, F, and CO.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/46509503/table_003.jpg)






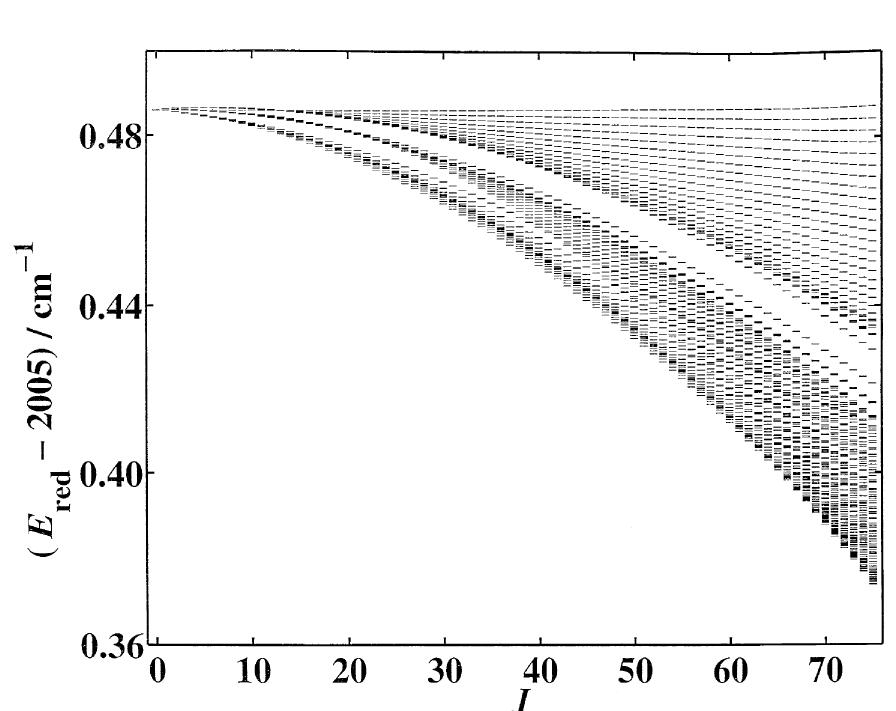

![Fig. 6. Detailed portion in the R-branch of the vg band of Mo(CO), compared to the simulation. To get correct line intensities in the simulation and, more precisely, a good P-branch/R-branch intensity ratio, we found that it was necessary to develop the dipole moment operator up to the first order, that is to include a small Herman- Wallis [11] term. The values](https://figures.academia-assets.com/51114234/figure_005.jpg)


![Hamiltonian and dipole moment effective parameters for the vg band of Mo(CO)g. The standard deviation is given in parenthesis, in units of the last two digits. J max is the maximum J value assigned and o is the root mean square deviation of the fit. For the relationship between our notation and that of Robiette et al. [16], see Ref. [11]](https://figures.academia-assets.com/51114234/table_002.jpg)




![different valence bond configurations [25]. More precisely, the A, ‘magnetic flux’ determines ‘IG. 4: Caricature of a spin liquid state. The valence bonds are entangled between different](https://figures.academia-assets.com/33774795/figure_004.jpg)
![FIG. 5: Histogram of the VBS order parameter defined in | 12 in the numerical study [19] b ndvik of Ho + Hy. The circular symmetry is emergent and implies a Goldstone boson which is the emergent photon A,.](https://figures.academia-assets.com/33774795/figure_005.jpg)











